Virtual Reality Active Games as a Potential Tool to Enhance Movement Skills and Promote Participation in Physical Activities for Children with DCD: Pilot Study-Juniper Publishers
JUNIPER PUBLISHERS-OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL OF INTELLECTUAL & DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES
Abstract
Children with developmental coordination problems exhibit difficulties performing even seemingly simple motor tasks, discouraging them from engaging in age appropriate physical activities. It appears that playing active video games may have a positive impact on certain aspects of their motor performance and the willingness to be physically active. The purpose of the present pilot study was to examine if these positive effects can be evident in two children with Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD) playing selected Xbox Kinect sports games. One eleven year old boy and a nine year old girl, diagnosed with DCD, were assessed using Movement Assessment Battery for Children (MABC2) and selected components of Bruininks Oseretsky Test (BOT2) at pre, mid, and post sessions, and two weeks after the program. Children engaged in Wake Racing, Climbing, Soccer, and Tennis games, in two 40-minute sessions per week, for 6 weeks. The parents and the children were also involved in an interview at the end of the study. The results from the formal assessment tools showed that both children improved in balance and ball skills subsections of the MABC2. However, the data from BOT2 failed to show the expected effects on running speed and agility, and in the strength domain. The interviews with children revealed that playing games was enjoyable and could potentially affect their willingness to take part in active play. This was confirmed by parents, who also were interested in implementing this protocol within the home setting. However, the degree to which the skills acquired/refined while playing active video games transfer to real-life tasks requires further investigation.
Keywords: Developmental coordination disorder; Innovative clinical treatment; Movement skills; Motor abilities
Introduction
Video games undeniably represent one of the most popular sources of entertainment for children and adults of all ages. They are available on a large spectrum of systems, from consoles accompanied to televisions, hand held devices, and mobile phones. In fact, 32% of 2-7 year olds and 65% of 8-18 year olds in America have television sets accompanied with some sort of video games [1]. This is troublesome for many health professionals who rightly perceive the engagement in such games as yet another barrier to being active, particularly for children [2]. Nevertheless, despite these concerns research has shown that if the games involve active movements they may actually have positive effects on the acquisition or relearning of certain motor skills [3]. This is not to say that video-games will or should replace the time spent engaging in active and meaningful physical activities. However, these games offer an opportunity to learn the basic movement skills in an environment that is non–threatening, fun, supportive and engaging. Thus, such games may represent a temporary but valuable alternative for individuals who are often unwilling to engage in active play/activities due to their low skill or fitness levels and coinciding low perceptions of competency and feelings of social unaptness.
From the clinical perspective, implementation of active virtual games (Sony's PlayStation, Nintendo Wii, and Microsoft Xbox Kinect) constitutes a useful approach as many individual, task and environmental constraints can be altered to assure success. Also, the fact that the performer has the opportunity to practice a number of distinctive skills, or perform a singular skill under different task and/or environmental-virtual conditions, is conceptually relevant. The former condition is synonymous with the premise of contextual interference [4], whereas the former approach is in line with schema theory and variability of practice hypothesis [5], two of the most robust concepts in contemporary motor learning literature. It has been also suggested that the implementation of virtual games may stimulate implicit learning and positively affect the variety of perceptual motor domains which otherwise would be difficult to enhance if the child was unwilling to take part in any physical activity [6]. These positive effects have been evident in studies involving children with Down syndrome [7], attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) [8] and those without any known medical conditions but who are overweight [9]. Also, there has been some initial research carried out with children diagnosed with Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD), however the results remain equivocal.
Children with DCD account for 6 to 10% of school aged children and exhibit movement problems that are due to factors other than known medical conditions or intellectual disability [9]. Also, they exhibit motor learning difficulties [10] which prevent them from acquiring or mastering different motor abilities (e.g. agility, strength, hand-eye coordination), as well as fundamental (e.g. throwing, catching, balancing) and specialized movement skills (e.g. activities of daily living). Due to these movement constraints they exhibit repeated failures when performing even seemingly simple tasks. As a result, they often are ridiculed and bullied, becoming reluctant to participate in physical activities in socially relevant contexts (school, playground; sport settings). This further deteriorates their movement repertoire and jeopardizes their chances of meaningful interaction with their peers [11].
In regards to children with DCD and virtual active games the existing research is valuable, but still relatively limited. Gonsalves [12] reported that when engaged in the active video games children with DCD carried out the tasks differently when compared to their typically developing peers. This is a positive Instrumentation finding as it indicates that the activity affords the participant to explore different and possible adaptive movement patterns to accomplish the task at hand. In terms of the other investigations, some failed to show the expected positive effects [13] whereas others revealed that virtual games may in fact constitute an effective clinical tool [14-16]. Among the different aspects of motor functioning there is a robust trend showing that playing active video games has a positive effect on balance control. Also, the anecdotal reports from parents indicated that participation in these games positively transferred to children's ability to play ball games and perform agility and strength related playground skills [17]. However, the available research is still limited as the scope of previous studies focused primarilyon Nintendo's Wii games. Thus it is plausible that different types of virtual reality active games may have positive effects on aspects of motor functioning, other than balance control. Also, a more in depth qualitative analysis of parents' and children's perceptions of the effectiveness and applicability of such approach may provide useful information to researchers and clinicians. As a result, the first purpose of this study was to examine if playing active virtual motion Xbox Kinect games had positive effect on balance control, ball skills, agility and strength in two children with DCD. The secondary objective was to infer whether participation in such games was enjoyable and motivating, based on the perceptions of the children, and if this approach was effective and worth implementing at home, as inferred from parents.
Materials and Methods
Participants
One male (11 years of age) and one female (9years of age), diagnosed with DCDby a qualified health professional, were recruited via purposive sampling. They did not exhibit vision problems (e.g. required prescription lenses), and had no previous experience with active virtual games. Also, in order to take part, the parents were asked to refrain their children from any other clinical programs for the duration of the study.
Instrumentation

Kinect system for Microsoft's Xbox 360(Microsoft Inc, Redmond, Washington, USA) was implemented. The user stood facing the TV-screen where the virtual gaming environment was displayed. In this video-capture technology the user does not need any other game controller than naturalistic body movements. A video camera plugged into the gaming console placed a real-time 3D image of the user inside the simulated environment where he/she can move around and interact with virtual objects (Figure 1). Four games were utilized in this study. The game of Tennis involved intercepting and striking the ball thus training one's hand/eye coordination and perceptual- motor integration. The second game was soccer requiring the participant to manoeuver the body to correctly time a kick when the ball was approaching. It is a full body movement involving inter-segmental coordination between the upper and lower body. In the Wake Racing game the participant was represented on the screen as sitting on a Seadoo. The child was required to balance his/her body to manoeuvre the Seadoo around the track. The last game played was Climbing, where the child had to maintained the arms above the head and simultaneously grab for the next hand hold and pull down with the opposite hand to scale the wall. The child was also required to jump to grab for higher hand holds. This game constrained the participant to implement strength, stamina and agility.
Outcome measures
The Movement Assessment Battery for Children (MABC-2) [18] was used to examine the proficiency in balance control and interceptive ball skills. Manual dexterity was not examined as conceptually there is no link between the activities undertaken and the child's ability to perform fine motor skills. The balance control section was comprised of three items (one-leg standing; walking on the line; jumping) while aiming and catching included two tasks, one related to the respective domain. Each raw score was transformed into a standard score for each task. Generally, the sum of all eight items can be utilized to derive a total standard score and a percentile score. However for this study, only individual standard scores for each section were used as manual dexterity was not tested.
Selected subsections of Bruininks Oseretsky test of motor proficiency (BOT2) [19] were also implemented. The BOT2 encompasses a large spectrum of fine and gross motor skills, however for the purpose of this study only running speed and agility as well as strength sub-sections were considered. Both the running speed and agility and strength portions of the test consist of five tasks. The raw point score for each task was converted into total point score, which was subsequently converted into a scale score.
Qualitative interview
A semi-structured interview was conducted with both parents and children. A thematic (deductive) interview approach was implemented, utilizing open-ended questions. When interviewing the parents, three main areas of interest were identified. First, the potential changes in the exercise habits of the children were explored. Also, the impact that the intervention had on the child's motivation to participate in physical activity in general, and overall enjoyment of active gaming was inferred. Lastly, the parents were asked about their perception of the usefulness of this approach and the potential to its implementation within the home setting. The interviews lasted approximately 45 minutes.
Procedure
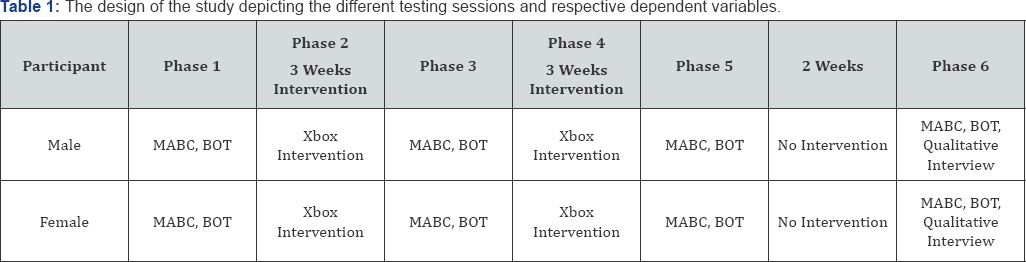
The study consisted of six phases (Table 1). In Phase 1, MABC and BOT2 were implemented, as baseline measures. In Phase 2, each participant attended 60-minute sessions twice a week for a period of six weeks, involving virtual games on the Xbox Kinect utilizing the Kinect Sports Rivals game. The primary researcher oversaw all the sessions. The Xbox Kinect system was the training tool. Twenty minutes were allotted for tennis, soccer, wake racing, and climbing games. The same measures that were taken during Phase 1 were administered once again at the three-week mark representing a mid-assessment session (Phase 3). Phase 4 involved additional 3 weeks of intervention, and post-test (Phase 5) was implemented at the end of this time period once again using MABC and BOT2 tests. The retention test (Phase 6) was implemented to infer whether the changes in performance, as inferred from the formal assessment tests, were permanent. Also, qualitative interview with both the child and parents took place during this phase Table 1.
Design and data analysis
A case study approach was utilized, with testing time (pre–assessment, mid-assessment, post-assessment, and retention test) as the independent variable. The dependent variables were the scores gathered through the implementation of the MABC-2 and BOT-2 tests across the different phases of the study. In both tests higher scores represented better performance. Also, the information gathered through the qualitative interviews was utilized to infer the potential effects of gaming on psychological constructs such as motivation and enjoyment.
Results
Outcome data
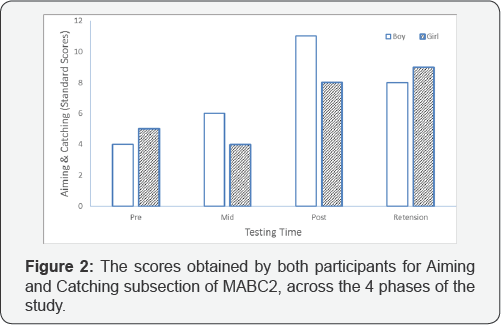
The standard scores from MABC-2 were used to infer the potential changes in two areas of motor proficiency. In terms of ball skills, as evident from the pre-test data (Figure 2), both children exhibited low skill level. The scores of 4 and 5 coincide with 2nd and 5th percentile respectively, according to the norms provided in the manual [18]. At the post-test, the scores increased considerably, particularly for the male participant whose standard score of 11 corresponds to 63rd percentile. A similar scenario was evident in the performance of the female whose score of 8 placed her at 25th percentile. As evident from the retention test, the enhanced performance was relatively permanent as the scores although lower for the male, were still considerably higher as compared to their initial ball skill status.
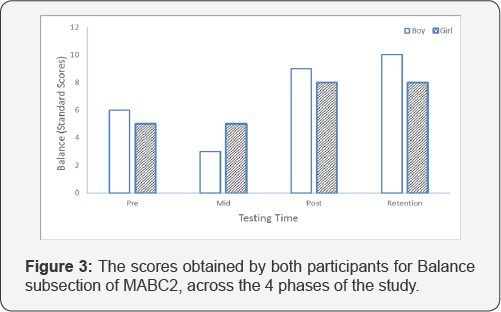
The analysis of balance scores (Figure 3) showed a similar scenario as compared to the aiming and catching domain. As evident, both children exhibited scores that would place them at/around the 6thpercentile at the pre-test, indicating low skill level. However, the data collected at the post-test showed a substantial increase in their balance skills, placing them at 63rd and 25th percentile, respectively. The retention test supported that these improvements were permanent.
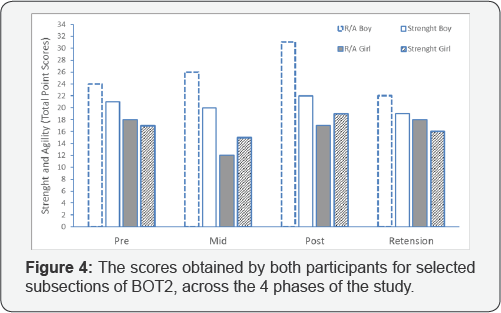
In order to infer if active video games had an impact on different aspects of motor performance, namely, strength and running speed/agility, two subsections of Bruinkins test were implemented. The scores (Figure 4) showed an equivocal scenario. As evident at the pre-test, the male participant was slightly more capable in the two domains as compared to the female, but both were relatively stable across the two areas. Considering that 52 and 42 are the highest possible scores for running speed/agility and strength, respectively, it is evident that both children exhibited a low skill level in these domains. At the mid- and post sessions, aside from the running and agility score for the male, the other values remained relatively comparable to those achieved at the pre-test. The examination of the retention scores confirmed that the performance was not enhanced as compared to the pre- and post-tests' scores.
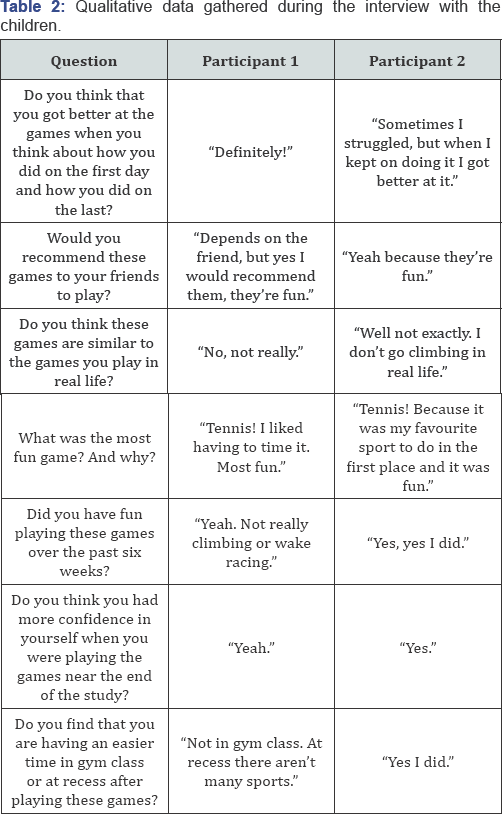
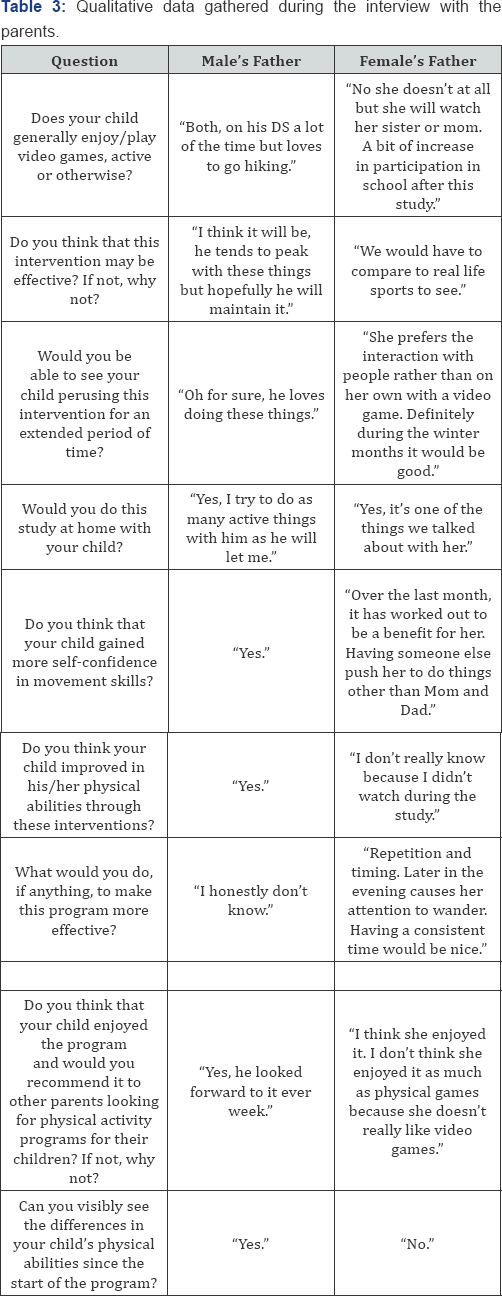
In order to infer if the children and parents perceived this kind of approach as effective and promising for the future implementation, interviews involving open-ended questions were carried out. The information conveyed by the children is presented in Table 2, whereas the information gathered from the parents is presented in Table 3.
Discussion
Outcome data
The objective of the current pilot study was two-fold. The first was to examine the effects of playing active virtual motion (Xbox Kinect) on balance control, agility and performance of core movement skills in two children diagnosed with Developmental Coordination Disorder. The emerging results were mixed.
The analysis of MABC-2 scores showed substantial improvements in ball skills and balance control for both children. In terms of the first domain, when the normative data was reviewed it was evident that both children improved from being below 10 percentile to 63rd and 25th respectively, as inferred from MABC-2 norms. Even when considering the measurement error associated with individual sub-sections, such change in scores has to be considered as "real" These positive changes were seen gradually over the initial part of the study, and then at the retention tests confirming that these improvements were relatively permanent. Intuitively, when considering the nature of the games being played (e.g. tennis), generating such actions effectively does force the player to implement good hand-eye coordination, interceptive (timing) skills and suitable intra-limb coordination between the different joints of the arm involved. All these underlying abilities are also critical in manual skills regardless if they are occurring under external time demands (e.g. catching) or are self-paced (e.g. aiming and throwing). Thus, the implementation of the tasks included in MABC-2 allows to make inferences in regards to the generalizability/transferability of the skills practiced via virtual games to real-life tasks. These results do not confirm previous findings [13,14,16], which showed no substantial changes in this domain as inferred from MABC-2. However, it should be noted that these investigations implemented a Wii Fit program, whereas this study involved Xbox system. It is plausible that the degree to which the virtual games are effective may be constrained by the type of the games played, as well as the technology used. The games available in the market vastly differ in terms of type of movements they allow and the nature of the interaction with the screen and surrounding environment [20].
The inferences emerging from the ball skills were in line with those involving balance control tasks. Both children were positively affected by the virtual games played, and considering their nature it can be speculated that soccer and wake racing activities contributed to these improvements. Although conceptually balance control is a specific skill rather than a general motor ability [21], the changes in MABC-2scores were not surprising since the tasks involved in the test (e.g. standing on one foot) are comparable to those involved in the games (e.g. standing on one leg while attempting to kick the virtual ball). In relation to previous research involving balance control tasks/ measures once again the inferences were mixed. Straker et al. [13] showed no changes in balance control as inferred from MABC and COP measures. However, the expected effects were evident in the studies by Jelsma and colleagues involving static [16] and dynamic balance tasks [22], as well as in other studies showing improved balance control as measured via MABC-2 and BOT-2 tests [14]. Collectively, it appears that among all the motor domains that are possibly affected by the virtual games, regardless of the type of the game or the system implemented, the positive effects on balance control are robust across majority of the studies.
The analysis of the BOT-2 scores, in regards to strength and running speed/agility, showed a different scenario. The review of the scores (Figure 4) showed that both children varied greatly across the testing sessions, even if the male participant was performing slightly better. This may be due to his age and likely gender. However, as evident from the retention tests, the scores were comparable or even lower than those obtained at the pre–test, indicating that the changes emerging during the study were not due to “true” learning. These results are in line with previous research examining these domain via subsections of BOT-2 [15], as well as other measures of speed/agility such as 2min walk test [23] and 20m shuttle run test, as well as strength [14]. Although at face value it is somewhat surprising that certain domains are affected by the active virtual games, whereas others are not, conceptually and intuitively these results are logical. Among the different physical proficiency domains, as outlined by Fleishman [24], abilities such as speed of movement, gross body coordination, stamina and strength represent different aspects of motor functioning. Thus if the games implemented in the intervention are geared more towards interceptive/timing or perceptuo-motor tasks, the domains such as strength or running speed should not be affected. Stated differently, the nature of the games implemented is an important constraint which needs to be considered given the needs of the persons involved in the intervention.
Qualitative data
In order to infer if the children and parents perceived this kind of approach as effective and promising for the future implementation, interviews involving open-ended questions were carried out. The information conveyed by the children showed an overall positive outlook towards the games, from the stand point of enjoyment and future participation. However, they were also sceptical in regards to how, or if, these tasks were similar to those performed in real-life. In terms of how the skills practised here would translate into enhancement of their motor performance in every-day physical activities, the responses varied. The interview with parents revealed that both children had mixed interest in the video-games which may impact how much they have gained from the sessions. However, they confirmed that playing such games was enjoyable for the children and that they may have a positive impact on their motor performance. However, they also stressed that importance of transferability to real-life situations, and the fact that playing games alone takes away from interaction with other kids. Also, although both indicated that they would try this approach at home, by the end of the study only parent acknowledged a potential change in the child's physical capabilities.
Conclusion
The results of this pilot project although warrant caution due to small sample size contributed to the existing knowledge base. It was shown that Exbox games, just like the Wii system implemented in previous studies, resulted in positive changes in motor proficiency. However, the results from this and previous investagions also showed that the nature of the resulting perceptuo-motor effects is specific to certain domains and not others (e.g. stamina; strength). Thus the nature of the tasks implemented in the games, along with the individual constraints of the participants, represent an important factor that the clinicians or parents should consider when implementing these games. From the stand point of enjoyment, motivation and feasibility for future implementation, both children and parents had very positive outlook. However, the questions regarding the transferability of the skills acquired via gaming to real life tasks is still unclear. Also, the fact that these games are often played in isolation does not enhance or affected the social dynamics and sense of belonging which can be achieved during free play Although virtual gaming presented in group setting would take away from the experimental control of the study, from the practical perspective it may enhance child's enjoyment of the games, stimulate effort and the necessity for establishing and maintaining social interactions with peers of same/similar age and skill level. In summary, the evidence seems to support the use of active video games as an enjoyable medium for self–directed physical activity of light to moderate intensity. However, as emphasized earlier, playing active video games should not be considered as a replacement of vigorous sport activities, but rather as a possibility to convert time spent on passive/ sedentary gaming to more active routines.
For more Open Access Journals in Juniper Publishers please click on: https://www.crunchbase.com/organization/juniper-publishers
For more articles in Open Access Global Journal of Intellectual & Developmental Disabilities please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/gjidd/index.php
For more Open Access Journals please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com
To know more about Juniper Publishers please click on: https://juniperpublishers.business.site/



Comments
Post a Comment