A Study on Human Error Recovery Effect by Strengthening Follow-up System among Workers in Team Work-Juniper Publishers
Global Journal of Intellectual & Developmental Disabilities (GJIDD)
Railway companies aim to improve enterprise value by providing railway services to ensure users safety and peace of mind. Thus, in safety activities, the purpose is derived not only from accident prevention activities but also for lifting up motivation of employees. Among such safety activities, there is "the strategy of establishing the follow-up system” that some companies promote. This strategy is to establish and strengthen a follow-up system, which is an organizational system with a posture to prevent small errors and carry out tasks smoothly by helping each other as a team. This paper provides an analysis method for the progress of retention rate of the follow-up system and change in consciousness to safety activities to clarify a group with behavior posture of voluntary follow. Moreover, this paper aims to create an advice list for actual work in 10 categories on the basis of these results.
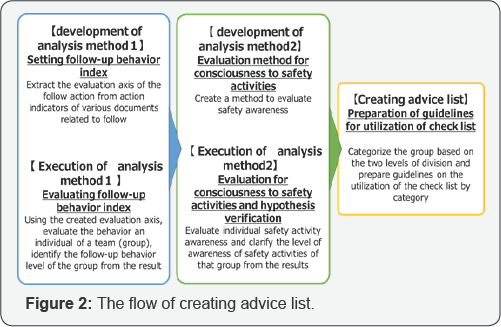
The Flow of Creating Advice List
First, we extracted six items of follow-up behavior
index ("Goal achievement ", "Group maintenance”, "Positive”, "Critical”,
"Consideration”, "Interpersonal assistance”) by referring to action
indicators in four fields ("Followership”, "Leadership”, "Organization
citizen behavior”, "CRM skills”) and comparing them with actions that
can be realized in the actual site.
Then, we developed an analytical method to evaluate
the progress of it by preparing evaluation algorithm of five grades for
each of the six indicators and evaluating the remarks in the discussion
which is part of the safety activities in the actual enterprises.
Then, based on the basic model that the progress of
it influences the change in the consciousness to safety activities of
employees, we developed an analytical method to verify the change of
companies whose follow-up system has been established.
Then, consciousness to safety activities is divided
into four groups "collective cohesiveness” "aggressiveness” "check
system” "trouble countermeasure”. In addition, we executed multilevel
analysis, hierarchical linear modeling and a simple effects analysis to
the data of the survey of the consciousness. Finally, based on the two
analytical methods, we created a group classification table of 10
categories and an advice list aiming at utilization of check lists in
each category.
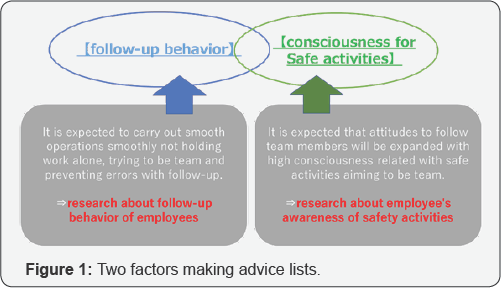
In conclusion, the analysis method and advice list
prepared in this study indicated the possibility of clarification a
group with behavior posture of voluntary follow. Identify employee's
awareness of safety activities (Figure 1 & 2).
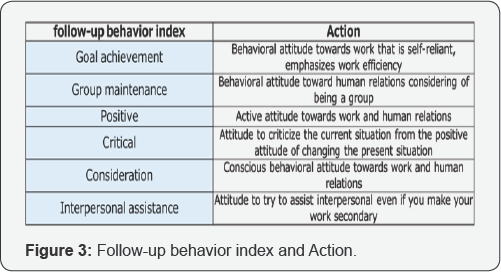
Setting follow-up behavior index
I set six behavior index, "Goal achievement”, "Group
maintenance”, "Positive”, "Critical”, "Consideration”, "Interpersonal
assistance”. It is desirable that these action indicators are kept in
good balance. We can see the action attitude from three perspectives.
First, focusing to "Goal achievement "and "Group
maintenance”, these show the view point that emphasizes in carrying out
tasks. We can grasp whether the organization or the employee is a
behavioral attitude to prioritize work, a behavioral attitude to
prioritize human relations, or a behavioral posture to think both in
balanced way
Second, focusing to "Positive” and "Critical”, these
show the attitude towards work and group. Comparing to two index, It is
possible to grasp the behavior attitude whether the organization or the
employee active or critical to group and try to get better group status.
Finally, focusing to "Consideration” and
"Interpersonal assistance”, these show the attitude towards
interpersonal. If "Consideration” is high, the employee have
consideration to others. And if "Interpersonal assistance” is high, they
try to assist and help others (Figure 3).
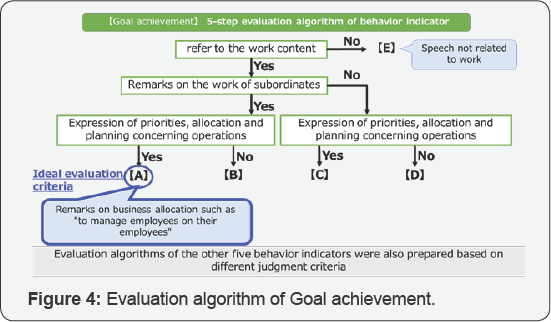
Evaluating follow-up behavior index
We prepare algorithm for evaluating six behavior indicators and classify into five stages A to E. Figure 4
introduce about "Goal achievement ". We classified employees who
evaluated by the algorithm into three groups of low behavioral awareness
people, middle behavior conscious people, high behavioral conscious
people. In the railroad company, it is aimed to raise low behavior
conscious people, so in this study, we focused on low behavior conscious
people and medium behavior conscious people.
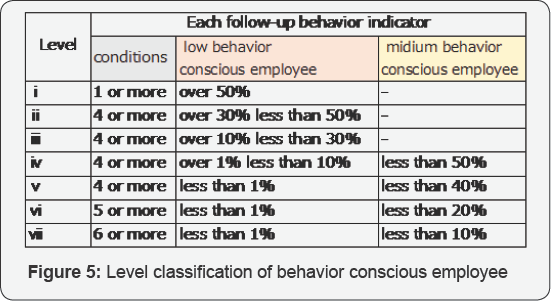
Then, based on the ratio of low behavior conscious
and medium behavior conscious, the follow - up behavior is classified in
order to prepare advice list for judging whether or not the checklist
can be used effectively in a workplace environment (Figure 4 & 5).
Evaluation method for consciousness to safety activities
We implement search system using for consciousness to
safety activities (HEMAS: Human Error Management Assessment System in
railroad company X.) HEMAS evaluate employee’s consciousness in score of
1 to 5 points.
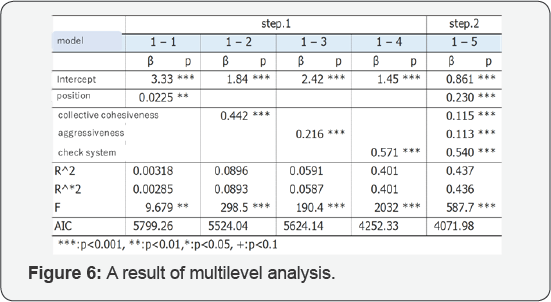
We executed multilevel analysis setting that response
variable is "trouble countermeasure” and explanatory variables are
"collective cohesiveness” "aggressiveness” "check system” "position”.
Evaluation for consciousness to safety activities and hypothesis verification
As a result of multilevel analysis, employee’s
"collective cohesiveness” "aggressiveness” "position”, especially "check
system” influence "trouble countermeasure”
Thus, the rising of employee’s consciousness for
trouble countermeasure lead to making work environment which can
checklists effectively.
y=0.861+0.230x1+0.115x2+0.113x3+0.540x4
y:Individual level troubleshooting awareness score
x1:Individual position (0 ...7: larger as the position is higher)
x2:Collective cohesiveness score of individual level
x3:aggressiveness score of individual level
x4:Consciousnes score for check system of individual level
(Figure 6)
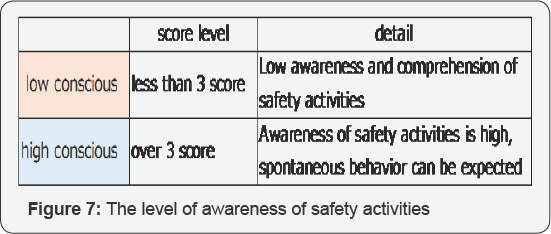
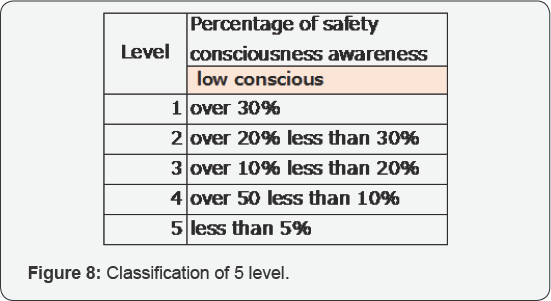
Based on the scores of HEMAS, we classified them as low conscious and
high conscious. In preparing guidelines for judging whether workplace
environments that can utilize checklists are available or not, we
divided the level of awareness of safety activities into five stages (Figure 7 & 8).
Creating advice lists
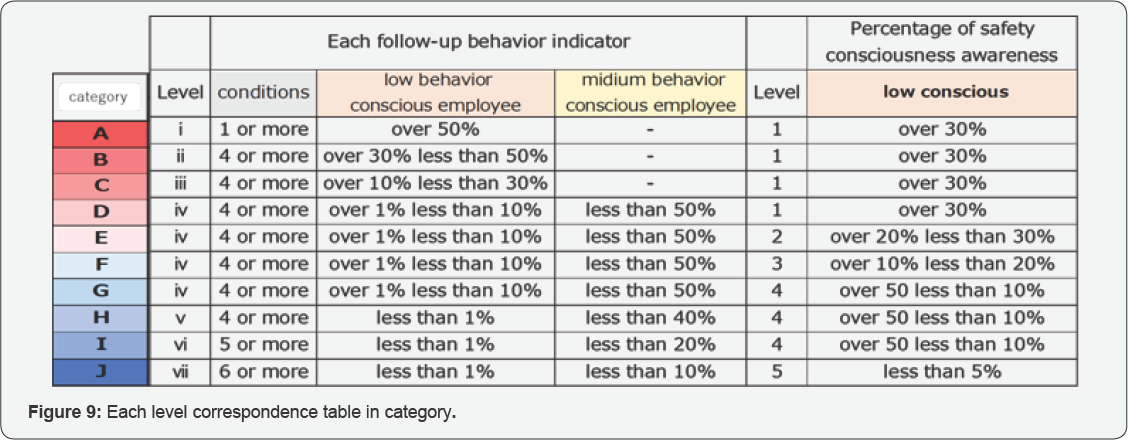
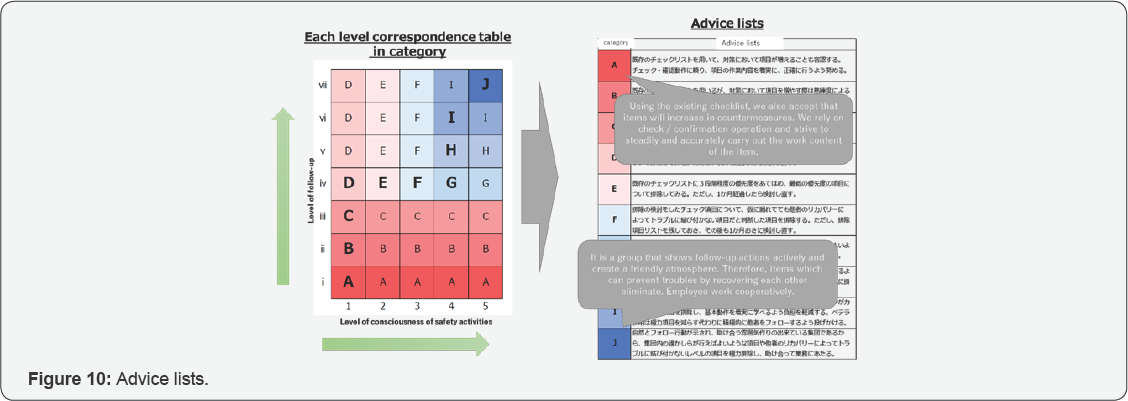
The table 9 of follow-up behavior revel connect the
table of consciousness to safety activities. Advice lists about the use
of checklists in each category are below (Figure 9 & 10).
Classification in Railroad Company
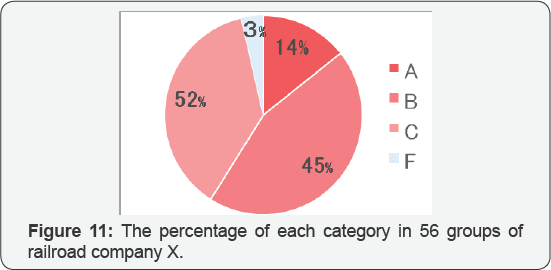
The percentage of each category in 56 groups of railroad company X is showed in Figure 11.
From the results, although the distribution varied, most of the groups
are belonging to categories B and C. Considering that the beginning of
the follow- up strategy was category A, we can see the work environment
is getting better, but it is still in the process of development.
Judging the maturity of the group of A to C, based on the advice list,
it turned out that "it is a group that should endeavor to accurately
perform the work content of the item using the existing checklist”.
Thus, it is found that the maturity level as a work environment where
follow-up actions can be taken is still low, and it is at the stage
where it should go using the checklist.
And, it is turned out that it is possible to create
an atmosphere to follow each other such as positively honoring voice at
operation department of driving section, which is one of the groups
belonging to the highest level category F. Therefore, advice list can
show accurate state of group.
We can showed the level of group which can use check
lists effectively making advice list. In a current situation, it was
also found that the check lists are more effective than the reduction of
the work load at railroad company X.


Comments
Post a Comment